|
Sustainable Design Awards Toolkit
Section 4.5 - Design for disassembly  This area covers products that are produced with disassembly in mind
therefore are easy to repair, upgrade and disassemble at the end of life.
An example of this would be a modular computer chassis like those produced
This area covers products that are produced with disassembly in mind
therefore are easy to repair, upgrade and disassemble at the end of life.
An example of this would be a modular computer chassis like those produced
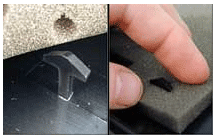 currently at 'Dell Computers'. No tools are needed to disassemble its
modular architecture, the covers are simply removed by pushing two
release buttons. The product is more economical having easy to use
fasteners on its removable individual components. The limited use of
screws with little adhesive, leads to easy maintenance and upgrade on
the product.
currently at 'Dell Computers'. No tools are needed to disassemble its
modular architecture, the covers are simply removed by pushing two
release buttons. The product is more economical having easy to use
fasteners on its removable individual components. The limited use of
screws with little adhesive, leads to easy maintenance and upgrade on
the product. |
||||||
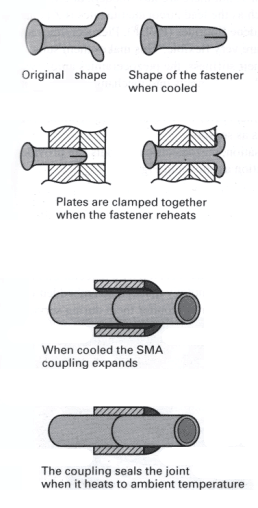
IBM are another leading company in the computer business that are considering and using more sustainable principles by considering disassembly in their products. IBM have stripped their machines of adhesives and now employ 'Dart' fasteners to hold foam in place of the less sustainable method. This is not only of benefit to the environment, IBM have also seen a number of benefits from this change intact. Assembly workers no longer have to deal with toxic fumes from the adhesives, IBM themselves no longer have to store or handle the hazardous materials - saving costs. Above all it improves the products' disassembly, it is easier to separate components that may be recycled. At present most products are disassembled using hand or robotic methods, and sadly neither are a huge consideration in the majority of products on the market. There are a few though for those who do consider it. The disassembly of a material may be improved is 'Active Disassembly' using Smart Materials, known as ADSM. The use of ADSM also allows for increased recyclability in consumer products to be integrated alongside the properties needed from the products' materials to fulfill its function. There are two main areas, Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) and Shape Memory Polymers (SMPs) that are being explored by various institutes regarding ADSM, Brunel University are at the forefront. The whole principle behind both sets of materials is that the specific material will change shape under a certain change of temperature specific to that material. The material is basically used as an actuator and various releasable fasteners to aid in disassembly are being investigated. Signs are that these could prove the future for better disassembly and for better products. |
||||||
Research into new technologies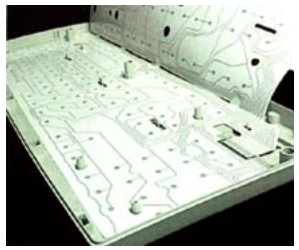 |
Dr Blue Ramsey of Brunel University's Department of Design (www.brunel.ac.uk) is developing research into social and technical issues involved in environmentally sensitive design. This is currently centred around new more sustainable methods for creating printed circuits using offset lithography to form the circulation paper & other flexible media. Dr. Ramsey's work is an example of the research and development going on throughout the world seeking more sustainable products and methods for the future. |
|||||
|
||||||
Inspirational Current Work
|
|||||||||||||||||
| � | |||||||||||||||||
Toolkit Index
  |